Most people tend to think of Diabetes as a single type of disease featuring too much sugar in the blood. The truth is that, on the contrary, diabetes is a group of many diseases that feature this condition. Despite having this condition in common, these diseases differ a lot – in their causes, symptoms, and treatment. In this article, we shall explain these differences.
The following are three types of Diabetes:
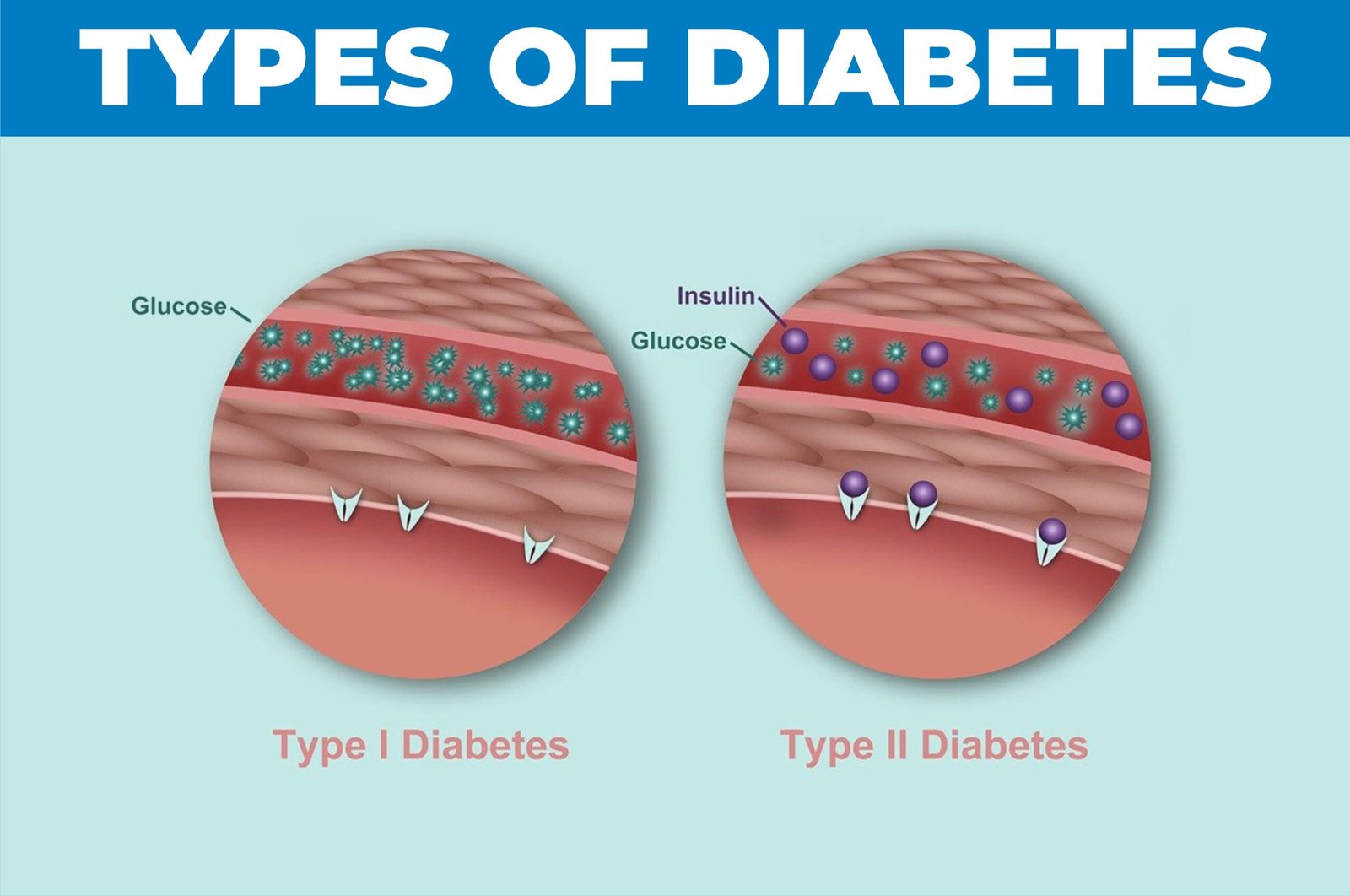
Type-1 Diabetes is a result of an autoimmune response in the body. In other words, a person’s immune cells attack their own cells – especially those that are supposed to create insulin in Pancreas. The result is that body can no longer create enough insulin or might not be able to create enough of it.
Prevalence – Type-1 Diabetes mostly appears at a younger age, mostly first noticed among children but it can show among adults too.
Symptoms – The following are some of the common symptoms of the disease – drowsiness or fatigue excessive thirst and hunger, frequent urination, dry, itchy skin, blurry vision (sometimes leading to blindness), weight loss, and slower healing of wounds. These symptoms are caused when type-1 diabetes results in what is called diabetic ketoacidosis – a condition causing these symptoms.
Treatment – Unfortunately, the damage to the pancreas is permanent. The patients must take daily doses of insulin to survive. Other treatments may be required if the symptoms mentioned above are showing. There is a need for continuous monitoring of this type of diabetes and insulin injections. These days there are some continuous monitor devices available.
When people talk about diabetes, this is normally diabetes they are talking about. 19 out of every 20 insulin patients suffer from this disease. It results from what is called insulin resistance – it is when insulin is no longer able to break down the sugar in the blood. That means both blood and insulin in your body build up until the body slows down the building of insulin. Meanwhile, sugar in the body keeps building up.
Prevalence – Very common. It used to normally show in middle age but these days it is showing even among children as a result of bad lifestyle choices. The bad lifestyle choices that may lead to type-2 diabetes include – consuming too many calories, not exercising enough, and drinking alcohol, Age, genetics, and obesity are known to be contributing factors. Other factors include pregnancy (see below), eating disorders, recent surgery, vessel diseases, etc. The condition called prediabetes (see FAQs below) suggests you are liable to develop this type of diabetes.
Symptoms – The symptoms are similar to Type-1 diabetes but are much slower to show.
Treatment – Unlike in the case of type-1 diabetes, insulin is not the answer. You will need medication. Healthier lifestyles with balanced diets and exercising are known to be great treatments, sometimes capable of reversing the disease.
Gastronomical Diabetes is a very rare kind of diabetes (often grouped the same as type=2 diabetes) and only happens during pregnancy. Apart from that, it is similar to type-2 diabetes. It is a big sign that the person has diabetes and is likely to develop type-2 diabetes in the future. That is known to happen in about fifty percent of cases.
There are several questions relating to different types of diabetes. The following are some of the most Frequently Asked Questions (F.A.Q.s) :
Question: What are the complications of type-2 diabetes?
Answer: The following are some of the complications of this disease:
Question: What is prediabetes?
Answer: Clinically, diabetes is only supposed to happen when sugar in the blood reaches particular levels. However, sometimes the blood sugar levels are high but not high enough to be considered diabetes. Such a condition is called pre-diabetes. The following are blood sugar levels categorized as prediabetes – blood sugar concentration is 100 to 125 mg/dL when fasting while the A1c test is 5.7% to 6.4% mg/dL. Lesser than these ranges are considered normal and higher than these are considered type-2 diabetes. If someone is diagnosed with type-2 diabetes then they may need to rethink their choices.
Question: When to see a medical practitioner?
Answer: If any of the above-mentioned symptoms are noticed, one should meet a practitioner to diagnose both diabetes and prediabetes. Either way, we recommend adopting a healthier lifestyle in consultation with your medical expert.
If the reader has any other questions, they should feel free to ask them here.
One can easily wrap up the above discussion by concluding that diabetes, whatever form it may take is a terrible disease. Those living with diabetes are forced to live a highly disciplined disease. If a person might be considered to be at risk of type-2 diabetes, they should get diagnosed to see if they have prediabetes.